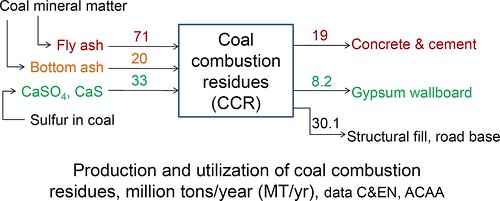
The cement industry is the single largest consumer of fly ash. This works, because blending flyash into clinker not only is beneficial economically, but also enhances durability of the concrete. However, low-NOx regulations resulted lower firing temperatures, which result in unburnt carbon in fly ash. Cement manufacturers could co-fire high-carbon fly ash in their kilns as a component of the raw kiln feed, provided that certain precautions are taken. Additionally, research at Penn State & the University of Nottingham has focused on using the unburnt carbons in the fly ash to capture mercury emissions from power plants. Fly ash can also be used to make bricks, The Greenest Brick Company being an example.
Environmental implications of coal combustion residue handling and disposal are critical, because of the potential for heavy metal contamination and other health issues. Therefore, enhanced utilization of coal combustion residues should be one component of environmentally responsible utilization of coal.